Understanding Thoracic Spine Syndrome: A Comprehensive Guide
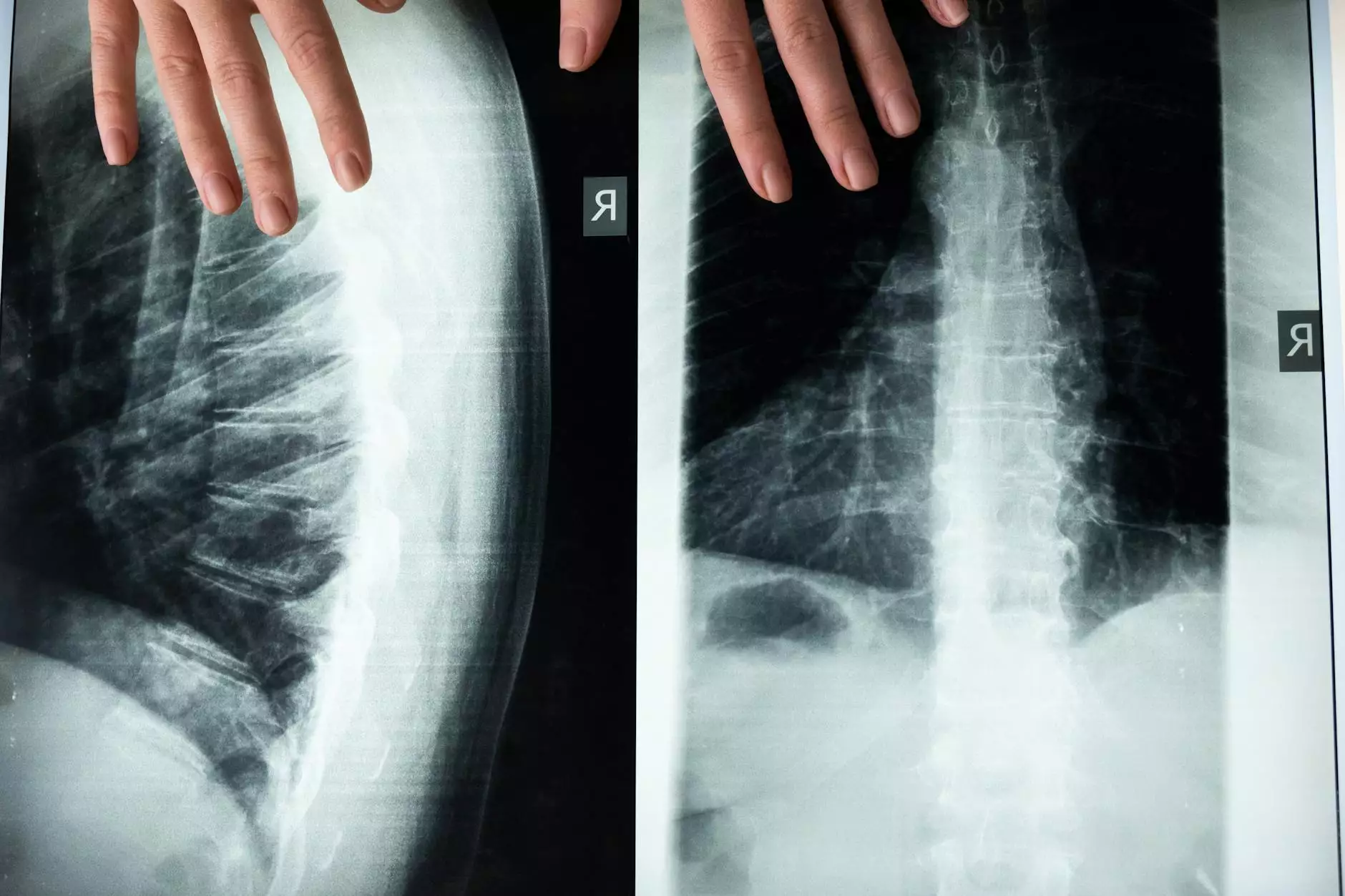
The thoracic spine syndrome is often an overlooked condition that can lead to significant discomfort and restrict daily activities. It involves the middle portion of the spine, specifically the thoracic vertebrae, which play a pivotal role in overall spinal health and function. This article aims to explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for thoracic spine syndrome, ensuring you have all the information necessary to take control of your health.
What is Thoracic Spine Syndrome?
Thoracic spine syndrome refers to a range of conditions that affect the thoracic region of the spine, which consists of 12 vertebrae located between the cervical spine in the neck and the lumbar spine in the lower back. This condition can result from various factors including injury, poor posture, and degenerative diseases. Understanding the complexities of thoracic spine syndrome is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Causes of Thoracic Spine Syndrome
Several factors can contribute to the development of thoracic spine syndrome, including:
- Poor Posture: Prolonged sitting or standing in incorrect postures can strain the thoracic spine.
- Injury: Accidents, falls, or sports injuries can lead to trauma in the thoracic area.
- Degenerative Disc Disease: Age-related wear and tear can affect the discs between the vertebrae.
- Herniated Discs: Bulging or ruptured discs can compress spinal nerves, causing pain.
- Muscle Strain: Overuse or lifting heavy objects can lead to muscle strain in the back.
- Osteoporosis: Weakening of bones can lead to fractures in the thoracic spine.
Symptoms of Thoracic Spine Syndrome
Identifying the symptoms of thoracic spine syndrome early is essential for effective treatment. Symptoms may vary depending on the underlying cause but commonly include:
- Pain: Localized pain in the mid-back region, which may radiate to other areas.
- Stiffness: A feeling of tightness or reduced flexibility in the thoracic region.
- Muscle Weakness: Weakness in the arms or legs due to nerve compression.
- Numbness or Tingling: A sensation of pinching, arising from nerve irritation.
- Difficulty Breathing: In severe cases, thoracic spine issues can affect respiratory function.
Diagnosis of Thoracic Spine Syndrome
To accurately diagnose thoracic spine syndrome, healthcare professionals employ various methods including:
- Physical Examination: A thorough assessment of posture, range of motion, and the area of pain.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans can help visualize structural abnormalities.
- Neurological Tests: These tests assess nerve function and can pinpoint areas of compression or damage.
Treatment Options for Thoracic Spine Syndrome
Effective treatment for thoracic spine syndrome often includes a combination of therapies aimed at relieving pain and correcting underlying issues. Some common treatment options are:
1. Physical Therapy
Working with a physical therapist can significantly improve spinal health. They can provide:
- Targeted Exercises: Strengthening muscles that support the spine.
- Posture Correction: Techniques to promote healthy body mechanics.
- Manual Therapy: Hands-on techniques to alleviate pain and improve mobility.
2. Chiropractic Care
Chiropractors can perform spinal adjustments to improve alignment and relieve nerve irritability. Regular chiropractic visits can lead to:
- Improved Range of Motion: Alleviating stiffness and enhancing flexibility.
- Pain Relief: Reducing discomfort without invasive procedures.
3. Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain. In certain cases, healthcare providers may prescribe:
- Muscle Relaxants: To ease spasms and discomfort.
- Prescription Pain Medications: For more severe pain management.
4. Injections
Corticosteroid injections may be recommended to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain in specific areas.
5. Surgical Options
In severe cases where conservative treatments fail, surgical interventions may be necessary to:
- Remove Herniated Discs: Relieving pressure on nerves.
- Stabilize the Spine: Through fusion or other surgical means.
Prevention Strategies for Thoracic Spine Syndrome
Preventing thoracic spine syndrome is often possible through lifestyle modifications. Here are effective strategies you can implement:
- Maintain Good Posture: Be mindful of your posture during daily activities.
- Ergonomic Workspaces: Arrange your workspace to promote spinal health.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in physical activities that strengthen back and core muscles.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration supports disc health.
- Limit Heavy Lifting: Use proper techniques when lifting heavy objects.
The Role of Education in Managing Thoracic Spine Syndrome
Education plays a vital role in managing thoracic spine syndrome. Understanding the condition empowers patients to take action. Educational resources, workshops, and support groups can provide:
- Insight into the Condition: Deeper knowledge of thoracic spine syndrome.
- Sharing Experiences: Engaging with others going through similar challenges.
- Access to Professional Guidance: Tools and strategies from healthcare providers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, thoracic spine syndrome is a significant health concern that can affect various aspects of life. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective management. By adopting preventative measures and seeking appropriate care, individuals can enhance their spine health and improve their quality of life. If you're experiencing symptoms associated with thoracic spine syndrome, consult with a healthcare professional to explore your treatment options today.
Learn More About Thoracic Spine Syndrome at IAOM
For more information on thoracic spine syndrome and how to effectively manage it, visit our website where we provide resources and support tailored to your needs.







